|
Home Page | Products | Contact Us | News & Events | Request Info. |
||||
|
|
Neutral Density Filter Information |
|
||
|
|
||||
|
|
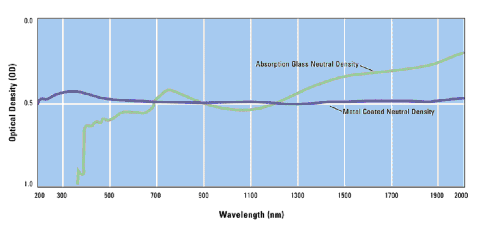
What are ND filters?ND or Neutral Density filters uniformly attenuate the intensity of light over a broad spectral range. This is achieved by either absorption using light absorbing glass or by a combination of absorption and reflection using a thin-film metal coating. Which type of ND filter should I use?Absorption ND filters are uncoated, gray tinted glass that attenuates entirely by absorption of the light. The degree of attention is determined by the thickness of the glass. They are not transmissive in the UV region and are generally only effective in the visible portion of the spectrum. As the absorption takes place in the filter glass these filters are less prone to surface damage than reflection filters. However as the degree of attenuation is a function of glass thickness it is not always possible to achieve the attenuation required for a given thickness and these filters tend to have greater batch to batch variability. Reflection ND filters attenuate by a combination of reflection and absorption. Made with Inconel® metallic coatings on glass substrates, this type of neutral density filter is much more uniform/neutral than the absorption glass filter and can be manufactured for a wider spectral range. See below for a comparison. Reflective ND filters can be used into the UV region of the spectra provided a fused silica substrate is used. The degree of attenuation is not so thickness critical.
How are they used?ND filters are used in numerous applications where the amount of light needs to be evenly reduced. Some applications are; Microscopy: ND filters reduce the intensity of the light source without affecting the spectral range of the source. They work like sunglasses, reducing the light intensity but without changing the colours. In fluorescence microscopy ND filters restrict the excitation intensity to minimise photo bleaching effects. Optical Calibration: When instruments are used to measure the amount of light being transmitted to a detector some form of calibration can be required. ND filters offer such a method. The introduction of traceable standard ND filters into the light path reduces the amount of light reaching the detector. Laser systems: ND filters find applications in several high-precision laser experiments. This is because the power of a laser cannot be adjusted without changing other properties of the laser light (e.g. parallelicity of the beam). Moreover, most lasers have a minimum power setting at which they can be operated. To achieve the desired light attenuation, one or more neutral density filters can be placed in the path of the beam. Photography: The purpose of standard photographic neutral density filters is to allow the photographer greater flexibility to change the aperture or exposure time, allowing for more control, particularly in extreme circumstances. What level of attenuation can be achieved?Neutral density filters attenuate spectral regions selected from 250 to 2500nm. The level of attenuation can be specified from optical density (OD) 0.04 to 4.0 where OD is defined as -log10 (T). For a table of ND vs %Transmission click here. Overall attenuation may be increased by stacking neutral density filters serially in the light path. For example, a 0.5 (OD 0.5) neutral density filter placed in series with a 0.3 (OD 0.3) neutral density filter will produce total attenuation of OD 0.8 (10-0.8) or 16% transmission. A six-filter set of 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0 optical densities can achieve a graduated range of spectrally neutral attenuation from OD 0.1 to 6.9. What is OD?OD or Optical Density is a measure of how much light is blocked by a filter. Optical Density-OD = -log10 (T). A filter with 1% transmission has an OD of 2 How are ND filters specified?An ideal neutral density filter reduces light of all wavelengths or colours equally but as we can see from the chart above this is not possible. ND filters are normally specified by reference to their blocking (OD) value at a wavelength of 550nm. An ND1 filter has an OD value of 1 and a transmission value of 1% at 550nm. All our ND filters are supplied with a spectral curve to enable filter performance across the transmission range to be validated. For a full specification of our ND filters please click here. How do I buy ND filters?From Glen Spectra, where else! For prices and details of our standard filters please click here. To request a quotation click here. To contact Glen Spectra please click here. If the filter ND level or size is not covered by our standard listing then please contact us for details on custom ND filters. Click here.
|
|
Back to top | Home Page | Products | Contact Us | News & Events | Request Info. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2007 Glen Spectra All rights reserved |
|